Tilapia vs Whiting
Tilapia and whiting are two types of whitefish that are often compared to each other. Both fish are relatively mild in flavor and have a firm texture. However, there are some key differences between the two fish. Tilapia is a freshwater fish, while whiting is a saltwater fish. This difference in habitat can affect the taste and texture of the fish. Tilapia tends to have a more earthy flavor than whiting, while whiting has a more delicate flavor. Tilapia is also a fattier fish than whiting, which can make it more flavorful but also more prone to spoilage. Whiting is a leaner fish, which makes it a healthier choice for people who are watching their weight.
Ultimately, the best fish for you will depend on your personal preferences. If you prefer a mild-flavored fish with a firm texture, then either tilapia or whiting would be a good choice. However, if you are looking for a leaner fish with a more delicate flavor, then whiting would be the better choice.
Tilapia vs Whiting
When comparing tilapia and whiting, several key aspects come into play, each highlighting different dimensions of these two fish. Let's explore nine crucial aspects:
- Species: Tilapia (Cichlidae family) vs Whiting (Gadidae family)
- Habitat: Freshwater vs Saltwater
- Flavor: Earthy vs Delicate
- Texture: Firm
- Fat Content: Tilapia (higher) vs Whiting (lower)
- Sustainability: Varies depending on farming practices
- Availability: Widely available
- Culinary Uses: Versatile, suitable for various cooking methods
- Nutritional Value: Good source of protein, omega-3 fatty acids, and vitamins
These aspects collectively shape the characteristics and culinary applications of tilapia and whiting. For instance, tilapia's earthy flavor and higher fat content make it ideal for dishes where bolder tastes are desired, while whiting's delicate flavor and leaner texture suit preparations that highlight its natural sweetness. Ultimately, the choice between tilapia and whiting depends on personal preferences and the specific culinary context.
Species
The species distinction between tilapia and whiting plays a crucial role in understanding their different characteristics. Tilapia belongs to the Cichlidae family and is native to Africa and the Middle East, while whiting belongs to the Gadidae family and is found in oceans worldwide. This difference in family and origin contributes to several key aspects that differentiate the two fish.
- Habitat: Tilapia are primarily freshwater fish, while whiting are saltwater fish. This difference in habitat affects their tolerance to salinity and their overall physiology.
- Flavor: Tilapia tends to have a more earthy flavor due to its diet and habitat, while whiting has a milder, more delicate flavor.
- Texture: Both tilapia and whiting have a firm texture, but tilapia may be slightly firmer due to its higher fat content.
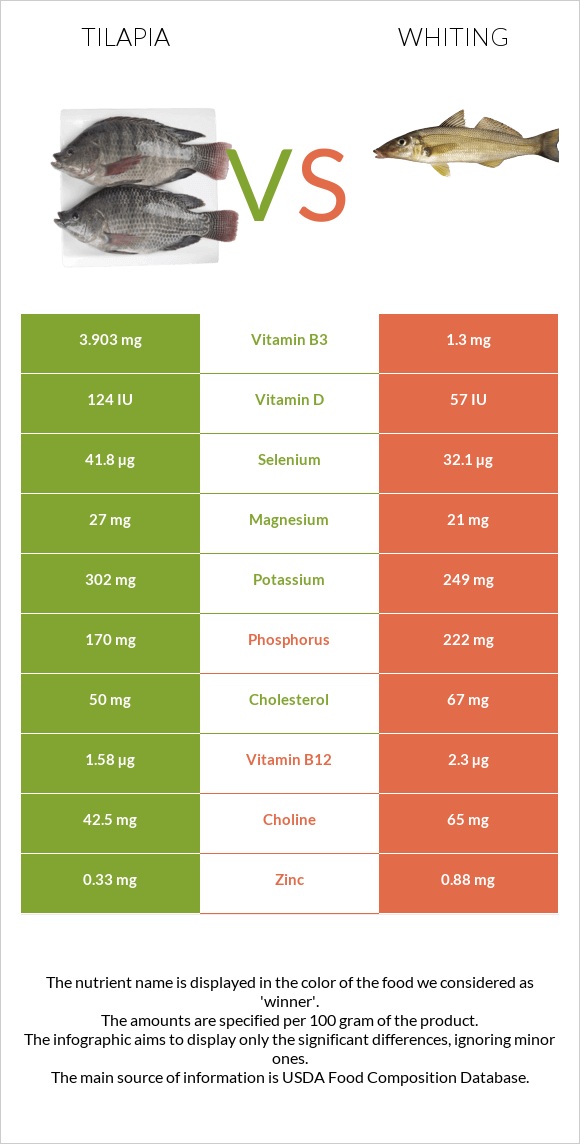
- Nutritional Value: Tilapia and whiting are both good sources of protein and omega-3 fatty acids. However, tilapia may have a slightly higher fat content and calorie count.
Understanding the species differences between tilapia and whiting is essential for culinary purposes. Chefs and home cooks can use this knowledge to select the most appropriate fish for their desired flavor, texture, and nutritional needs.
Habitat
The habitat of tilapia and whiting, whether freshwater or saltwater, significantly influences their physiology, flavor, and nutritional value. Tilapia, primarily found in freshwater environments, exhibit distinct characteristics that set them apart from whiting, which inhabit saltwater ecosystems.
Tilapia's freshwater habitat contributes to their earthy flavor profile. Their diet, consisting of plants and algae, imparts a unique taste that is often described as robust or muddy. In contrast, whiting, dwelling in saltwater, develops a milder, more delicate flavor due to their diet of small fish and crustaceans.
Beyond flavor, habitat also affects the nutritional content of these fish. Tilapia, living in freshwater, tends to have a higher fat content compared to whiting. This difference can be attributed to the availability of lipids in their freshwater environment. Whiting, on the other hand, being a saltwater fish, generally has a leaner composition with lower fat content.
Understanding the habitat-related differences between tilapia and whiting is crucial for culinary applications. Chefs and home cooks can leverage this knowledge to make informed choices when selecting the fish that best suits their desired flavor and nutritional preferences.
Flavor
The flavor profiles of tilapia and whiting exhibit a distinct contrast, with tilapia possessing an earthy flavor and whiting offering a delicate taste. This variation in flavor can be attributed to several factors, including their diet, habitat, and physiology.
- Diet: Tilapia's diet primarily consists of plants and algae, which imparts an earthy, slightly muddy flavor to their flesh. In contrast, whiting feeds on small fish and crustaceans, resulting in a milder, more delicate flavor.
- Habitat: Tilapia are predominantly freshwater fish, while whiting are saltwater fish. The difference in their aquatic environments contributes to the variation in flavor. Freshwater tends to have a higher concentration of minerals and organic matter, which can influence the taste of the fish.
- Fat Content: Tilapia generally has a higher fat content compared to whiting. This difference in fat content can also affect the flavor, with higher fat fish often exhibiting a richer, more robust taste.
- Cooking Methods: The cooking method can also influence the flavor of tilapia and whiting. For instance, grilling or pan-frying can enhance the earthy flavor of tilapia, while steaming or poaching may preserve the delicate taste of whiting.
Understanding the flavor differences between tilapia and whiting is essential for culinary purposes. Chefs and home cooks can use this knowledge to select the most appropriate fish for their desired taste preferences and cooking applications.
Texture
When comparing tilapia and whiting, texture is a crucial aspect that contributes to the overall eating experience. Both fish exhibit a firm texture, but there are subtle differences that can influence their culinary applications and suitability for various cooking methods.
- Muscle Fiber Structure: The firm texture of tilapia and whiting is attributed to the arrangement of muscle fibers within their flesh. These fibers are tightly packed and aligned, resulting in a cohesive and resilient texture.
- Collagen Content: Collagen, a structural protein, plays a role in determining the firmness of fish. Tilapia and whiting have a moderate amount of collagen, which contributes to their firm texture while allowing for some flexibility.
- Cooking Methods: The firm texture of tilapia and whiting makes them suitable for a variety of cooking methods. They can be grilled, pan-fried, baked, or steamed without losing their shape or becoming overly soft.
- Sensory Perception: The firm texture of tilapia and whiting provides a satisfying eating experience. When cooked properly, these fish offer a pleasant bite with a slight resistance, making them enjoyable to consume.
Understanding the firm texture of tilapia and whiting is essential for culinary purposes. Chefs and home cooks can use this knowledge to select the most appropriate cooking methods that will enhance the texture and flavor of these fish, ensuring a delicious and satisfying meal.
Fat Content
The fat content of tilapia and whiting plays a significant role in differentiating these two fish species. Tilapia generally has a higher fat content compared to whiting, which impacts their flavor, texture, and nutritional value.
The higher fat content in tilapia contributes to its richer, more robust flavor. This fat content also makes tilapia a more flavorful fish when cooked, as the fats render and enhance the taste. In contrast, whiting's lower fat content results in a milder, more delicate flavor, making it a good choice for those who prefer a lighter-tasting fish.
Furthermore, the fat content affects the texture of tilapia and whiting. Tilapia's higher fat content results in a slightly softer, more tender texture compared to whiting. This difference in texture is noticeable when cooking the fish, as tilapia may flake more easily than whiting.
From a nutritional standpoint, the higher fat content in tilapia means it is a richer source of omega-3 fatty acids. Omega-3 fatty acids are essential fatty acids that provide numerous health benefits, including reducing the risk of heart disease and inflammation.
Understanding the difference in fat content between tilapia and whiting is crucial for culinary purposes. Chefs and home cooks can use this knowledge to select the most appropriate fish for their desired flavor, texture, and nutritional needs. For instance, if a recipe calls for a fish with a bolder flavor and a more tender texture, tilapia would be a suitable choice. Conversely, if a recipe requires a milder-tasting fish with a firmer texture, whiting would be a better option.
Sustainability
In the context of "tilapia vs whiting," sustainability is a crucial factor to consider. Both tilapia and whiting can be farmed, but their sustainability practices vary greatly.
- Farming Methods: Tilapia is primarily farmed in intensive aquaculture systems, where high stocking densities and artificial feeding are common. Whiting, on the other hand, is often farmed in more extensive systems, with lower stocking densities and a reliance on natural food sources. Intensive farming practices can lead to environmental concerns, such as water pollution and disease outbreaks.
- Environmental Impact: Tilapia farming has been associated with negative environmental impacts, including habitat destruction, water pollution, and the spread of disease. Whiting farming, with its lower stocking densities and reliance on natural food sources, generally has a lower environmental impact.
- Feed Conversion Ratio: Tilapia has a relatively high feed conversion ratio, meaning it requires more feed to produce the same amount of fish compared to whiting. This can lead to increased pressure on wild fish populations, as fishmeal and fish oil are commonly used in aquaculture feed.
- Certifications and Standards: Several certifications and standards have been developed to promote sustainable aquaculture practices. When choosing between tilapia and whiting, consumers can look for products that are certified by organizations such as the Aquaculture Stewardship Council (ASC) or the Global Aquaculture Alliance (GAA).
By considering the sustainability practices associated with tilapia and whiting farming, consumers can make more informed choices about the fish they consume. Choosing sustainable seafood options helps protect the environment and ensures the long-term availability of these valuable resources.
Availability
The widespread availability of tilapia and whiting makes them popular choices for consumers around the globe. This availability is attributed to several key factors:
- Aquaculture: Both tilapia and whiting are widely farmed through aquaculture, which involves raising fish in controlled environments. Aquaculture has significantly increased the production of these fish, making them more accessible to consumers.
- Global Distribution: Tilapia and whiting are found in various regions worldwide, including Asia, Africa, Europe, and the Americas. This global distribution contributes to their wide availability, ensuring a steady supply to markets.
- Adaptability: Tilapia and whiting are adaptable species that can thrive in diverse environments. Tilapia, in particular, can be farmed in a range of water conditions, making it suitable for aquaculture in various locations.
The wide availability of tilapia and whiting has several implications:
- Consumer Accessibility: The widespread availability of these fish makes them accessible to consumers of all income levels. This accessibility contributes to the popularity of tilapia and whiting as affordable and convenient seafood options.
- Culinary Versatility: The availability of tilapia and whiting allows for their incorporation into a wide range of culinary preparations. Chefs and home cooks can easily find these fish in markets, enabling them to explore various recipes and cuisines.
- Nutritional Value: Tilapia and whiting are valuable sources of protein, omega-3 fatty acids, and other essential nutrients. Their availability ensures that consumers can access these nutrients through their diets.
In summary, the widespread availability of tilapia and whiting is a result of successful aquaculture practices, global distribution, and adaptability. This availability has significant implications for consumer accessibility, culinary versatility, and nutritional value, making these fish popular and valuable choices in the seafood market.
Culinary Uses
The culinary versatility of tilapia and whiting stems from their mild flavors and firm textures, making them suitable for a wide range of cooking methods. This versatility is a significant aspect of "tilapia vs whiting" as it contributes to their popularity and adaptability in various cuisines.
The mild flavor of both tilapia and whiting allows them to absorb marinades and seasonings well, making them ideal for grilling, baking, frying, and steaming. Their firm texture holds up well during these cooking methods, preventing them from breaking apart or becoming mushy. This versatility makes them suitable for various preparations, from simple pan-fried fillets to elaborate baked dishes.
For example, the delicate flavor of whiting makes it a great choice for delicate preparations such as ceviche, where the natural sweetness of the fish can shine through. Tilapia's more robust flavor, on the other hand, lends itself well to bolder preparations such as tacos or curries, where it can stand up to strong spices and flavors.
In summary, the culinary versatility of tilapia and whiting is a key aspect of their appeal. Their mild flavors and firm textures allow them to be incorporated into a wide range of cooking methods and cuisines, making them valuable additions to any home cook's repertoire.
Nutritional Value
When comparing tilapia and whiting, their nutritional value is a crucial aspect that sets them apart. Both fish are considered good sources of protein, omega-3 fatty acids, and vitamins, making them valuable additions to a healthy diet.
- Protein: Tilapia and whiting are excellent sources of protein, an essential nutrient for building and repairing tissues. Protein also plays a vital role in hormone production, enzyme function, and immune system regulation.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Omega-3 fatty acids are essential fatty acids that the body cannot produce on its own. They have numerous health benefits, including reducing inflammation, improving heart health, and supporting brain function. Both tilapia and whiting are good sources of omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA.
- Vitamins: Tilapia and whiting are also good sources of several vitamins, including vitamin D, vitamin B12, and niacin. Vitamin D is essential for bone health, while vitamin B12 is crucial for red blood cell formation and neurological function. Niacin is important for energy metabolism and skin health.
- Comparison: While both tilapia and whiting offer these nutritional benefits, there are some slight differences between them. Tilapia tends to have a slightly higher fat content than whiting, which may contribute to a higher calorie count. Whiting, on the other hand, may have a slightly higher protein content than tilapia.
In summary, the nutritional value of tilapia and whiting makes them both healthy choices for a balanced diet. Whether you choose tilapia or whiting will depend on your individual dietary preferences and nutritional needs.
FAQs on Tilapia vs Whiting
This section addresses frequently asked questions about tilapia and whiting to provide a comprehensive understanding of their differences and similarities.
Question 1:Which is better for health: tilapia or whiting?
Both tilapia and whiting offer nutritional benefits, including protein, omega-3 fatty acids, and vitamins. Tilapia has a slightly higher fat content, while whiting has a slightly higher protein content. Ultimately, the choice depends on individual dietary preferences and needs.
Question 2:Which fish has a stronger flavor: tilapia or whiting?
Tilapia has a more robust, earthy flavor compared to whiting, which has a milder, more delicate flavor. This difference makes tilapia better suited for dishes where bolder tastes are desired, while whiting is ideal for preparations that highlight its natural sweetness.
Question 3:Which fish is more versatile in cooking methods?
Both tilapia and whiting have a firm texture and mild flavor, making them suitable for a variety of cooking methods. They can be grilled, pan-fried, baked, or steamed without losing their shape or becoming mushy.
Question 4:Which fish is more sustainable?
The sustainability of tilapia and whiting depends on farming practices. Tilapia is often farmed in intensive systems with higher environmental impacts, while whiting is typically farmed in more extensive systems with lower environmental impacts. Consumers can look for certifications from organizations like the Aquaculture Stewardship Council (ASC) to support sustainable seafood practices.
Question 5:Which fish is more widely available?
Both tilapia and whiting are widely available due to extensive aquaculture practices and global distribution. Their availability makes them accessible to consumers of all income levels.
Question 6:Can tilapia and whiting be used interchangeably in recipes?
While tilapia and whiting have similar textures, their flavor profiles differ. In recipes calling for a mild-flavored fish, whiting can be a suitable substitute for tilapia. However, in recipes where a more robust flavor is desired, it may be preferable to use tilapia.
Summary: Understanding the differences and similarities between tilapia and whiting empowers consumers to make informed choices based on their taste preferences, nutritional needs, and sustainability concerns. Both fish offer unique culinary and nutritional benefits, making them valuable additions to a balanced diet.
Transition to the next article section: This concludes our exploration of tilapia vs whiting. In the next section, we will delve into specific culinary applications and provide tips for cooking these fish.
Tips on Cooking Tilapia and Whiting
To make the most of these versatile fish, here are some tips and tricks for cooking tilapia and whiting:
Tip 1: Seasoning and Marinating
Both tilapia and whiting benefit from simple seasoning. Salt, pepper, and a squeeze of lemon juice can enhance their natural flavors. For added depth, try marinating the fish in a mixture of herbs, spices, and olive oil before cooking.
Tip 2: Cooking Methods
Tilapia and whiting can be cooked using various methods, including grilling, pan-frying, baking, and steaming. Grilling or pan-frying gives a crispy exterior, while baking or steaming preserves their delicate texture.
Tip 3: Avoid Overcooking
Overcooking can result in dry and tough fish. Cook tilapia and whiting until they are just opaque throughout. Use a meat thermometer to ensure the internal temperature reaches 145F (63C) for tilapia and 135F (57C) for whiting.
Tip 4: Sauces and Toppings
Sauces and toppings can complement the flavors of tilapia and whiting. Try a simple lemon-butter sauce, a flavorful salsa, or a creamy dill sauce. Toppings like grilled lemon slices, fresh herbs, or crispy shallots can add an extra layer of taste and texture.
Tip 5: Pairings
Tilapia and whiting pair well with various sides. Grilled vegetables, roasted potatoes, or a fresh salad are excellent accompaniments. For a complete meal, serve with a side of rice or quinoa.
Summary: By following these tips, you can cook delicious and flavorful tilapia and whiting dishes that will impress your family and friends.
Transition to the article's conclusion: These versatile fish offer endless culinary possibilities, and with a little practice, you can master the art of cooking tilapia and whiting to perfection.
Conclusion
This exploration of tilapia vs whiting has highlighted the distinct characteristics and culinary applications of these two versatile fish. Tilapia, with its earthy flavor and higher fat content, stands out in dishes where bolder tastes are desired. Whiting, on the other hand, offers a delicate flavor and leaner texture, making it ideal for preparations that showcase its natural sweetness. Both fish are excellent sources of protein, omega-3 fatty acids, and vitamins, making them valuable additions to a balanced diet.
Ultimately, the choice between tilapia and whiting depends on individual preferences and the specific culinary context. Whether you opt for the robust flavors of tilapia or the delicate sweetness of whiting, these fish offer a range of possibilities to tantalize your taste buds. Embrace their versatility, experiment with different cooking methods and seasonings, and enjoy the culinary delights that tilapia and whiting have to offer.
Unveiling The Enigmatic "Canelo Wife": Discoveries And Insights
Uncover The Secrets Of Hailee Steinfeld's Net Worth: A Comprehensive Exploration
Unveiling Jason Statham's Weight: Unlocking Fitness Secrets And Beyond

ncG1vNJzZmiokZm2cnrApqpsZpSetKrAwKWmnJ2Ro8CxrcKeqmebn6J8tbXLmqeimV2rwG7Dx6KroqaXY7W1ucs%3D